Promise 对象代表了未来将要发生的事件,用来传递异步操作的消息。
一、Promise 基本特性
Promise 有三种状态:pending (进行中),fulfilled(resolve) (已成功),rejected (已失败)
Promise 对象接受一个回调函数作为参数,该回调函数接受两个参数,分别是成功时的回调 resolve 和 失败时的回调 reject;另外 resolve 的参数除了正常值以外,还可能是一个 Promise 对象的实例;reject 的参数通常是一个 Error 对象的实例
then 方法返回一个新的 Promise 实例,并接受两个参数 onResolved ( fulfilled 状态的回调),onRejected ( rejected 状态的回调,该参数可选)
catch 方法返回一个新的 Promise 实例
finally 方法不管 Promise 状态如何都会执行,该方法的回调函数不接受任何参数
Promise.all() 方法将多个 Promise 实例包装成一个新的 Promise 实例,该方法接受一个由 Promise 对象组成的数组作为参数 (Promise.all() 方法的参数可以不是数组,但必须具有 Iterator 接口,且返回的每个成员都是 Promise 实例),注意参数中只要有一个实例触发 catch 方法,都会触发 Promise.all() 方法返回的新实例的 catch 方法,如果参数中的某个实例本身调用了 catch 方法,将不会触发 Promise.all() 方法返回的新实例的 catch 方法
Promise.race() 方法的参数与 Promise.all() 方法一样,参数中的实例只要有一个率先改变状态就会将该实例的状态传给 Promise.race() 方法,并将返回值作为 Promise.race() 方法产生的 Promise 实例的返回值
Promise.resolve() 将现有对象转为 Promise 对象,如果该方法的参数为一个 Promise 对象,Promise.resolve() 将不做任何处理;如果参数是 thenable 对象(即具有 then 方法),Promise.resolve() 方法将该对象转为 Promise 对象并立即执行 then 方法;如果参数是一个原始值,或者是一个不具有 then 方法的对象,则 Promise.resolve() 返回一个新的 Promise 对象,状态为 fulfilled,其参数将作为 then 方法中 onResolved 回调函数的参数。如果 Promise.resolve() 方法不传入参数,会直接返回一个 fulfilled 状态的 Promise 对象。需要注意的是,立即 resolve() 的 Promise 对象,是在本轮“事件循环(event loop)”结束时执行,而不是在下一轮“事件循环”的开始时执行
Promise.reject() 同样返回一个新的 Promise 对象,状态为 rejected,无论传入任何参数都将作为 reject() 的参数
二、Promise 的优点
统一的异步 API
Promise 的一个重要优点是它将逐渐被用作浏览器的异步 API ,统一现在各种各样的 API ,以及不兼容的模式和写法。
Promise 与事件对比
和事件相比较,Promise 更适合处理一次性的结果,在结果计算出来之前或之后注册回调函数都是可以的,都可以拿到正确的值。Promise 的这个优点很自然。但是,不能使用 Promise 处理多次触发的事件。链式处理是 Promise 的又一优点,但是事件却不能这样链式处理。
Promise 和回调对比
解决了回调地狱的问题,将异步操作以同步操作的流程表达出来。
Promise 带来的额外的好处是包含了更好的错误处理方式(包含了异常处理),并且写起来很轻松(因为可以重用一些同步工具,比如 Array.prototype.map())。
三、Promise 的缺点
无法取消 Promise,一旦新建它就会立即执行,无法中途取消。
如果不设置回调函数,Promise 内部抛出的错误,不会反应到外部。
当处于 pending 状态时,无法得知目前进展到哪一个阶段(刚刚开始还是即将完成)。
Promise 真正执行回调的时候,定义 Promise 那部分实际上已经执行完了,所以 Promise 的报错堆栈上下文不太友好
四、简单代码实现.
最简单的 Promise 实现有 7 个主要属性,state(状态),value(成功返回值),reason(错误信息),resolve 方法,reject 方法,then 方法。
class版
class Promise{
constructor(executor){
this.state = 'pending';
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
let resolve = value=>{
if(this.state === 'pending'){
this.state = 'fulfilled';
this.value = value;
}
};
let reject = value=>{
if(this.state === 'pending'){
this.state = 'rejected';
this.reason = value;
}
};
try{
//立即执行函数
executor(resolve,reject);
}catch(err){
reject(err);
}
}
then(onFulfilled,onRejected){
if(this.state === 'fulfilled'){
typeof onFulfilled === 'function' && onFulfilled(this.value);
};
if(this.state === 'rejected'){
typeof onRejected === 'function' && onRejected(this.reason);
};
}
}
function版
function myPromise(constructor){ let self=this;
self.status="pending" //定义状态改变前的初始状态
self.value=undefined;//定义状态为resolved的时候的状态
self.reason=undefined;//定义状态为rejected的时候的状态
function resolve(value){
//两个==="pending",保证了了状态的改变是不不可逆的
if(self.status==="pending"){
self.value=value;
self.status="resolved";
}
}
function reject(reason){
//两个==="pending",保证了了状态的改变是不不可逆的
if(self.status==="pending"){
self.reason=reason;
self.status="rejected";
}
}
//捕获构造异常
try{
constructor(resolve,reject);
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
myPromise.prototype.then=function(onFullfilled,onRejected){
let self=this;
switch(self.status){
case "resolved": onFullfilled(self.value); break;
case "rejected": onRejected(self.reason); break;
default:
}
}
// 测试
var p=new myPromise(function(resolve,reject){resolve(1)});
p.then(function(x){console.log(x)})
//输出1
测试:
m = new Promise(resolve=>{
console.log('aaa')
setTimeout(function(){
resolve(9000)
}, 2000)
})
m.then(res=>console.log(res));//执行
运行起来我们发现只打印了构造函数中的 aaa 而 异步 then 方法并没有执行。
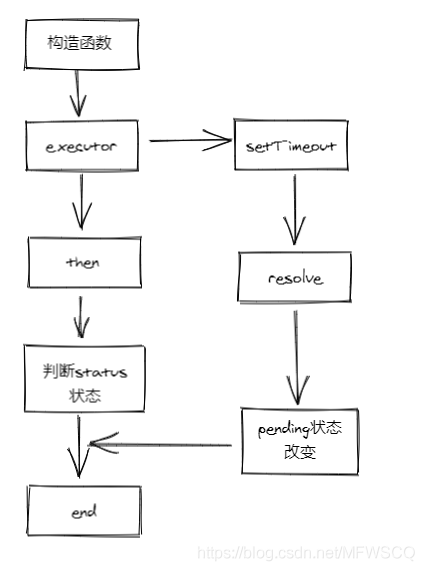
当then里面函数运行时,resolve由于是异步执行的,还没有来得及修改state,此时还是PENDING状态;因此我们需要对异步的情况做一下处理。
class进阶版
class Promise{
constructor(executor){
this.state = 'pending';
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
this.onFulfilled = [];
this.onRejected = [];
try{
executor(this.resolve,this.reject);
}catch(e){
this.reject(e);
}
}
resolve = (res)=>{
if(this.state === 'pending'){
this.state = 'fulfilled';
this.value = res;
this.onFulfilled.forEach(fn=>fn(res));
}
}
reject = (res)=>{
if(this.state === 'pending'){
this.state = 'rejected';
this.reason = res;
this.onRejected.forEach(fn=>fn(res));
}
}
then = (onFulfilled,onRejected)=>{
if(this.state === 'fulfilled'){
typeof onFulfilled === 'function' && onFulfilled(this.value);
}
if(this.state === 'rejected'){
typeof onRejected === 'function' && onRejected(this.value);
}
if(this.state === 'pending'){
typeof onFulfilled === 'function' && this.onFulfilled.push(onFulfilled);
typeof onRejected === 'function' && this.onRejected.push(onRejected);
}
}
}
function进阶版
const PENDING = "pending";
const FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const REJECTED = "rejected";
function Promise(excutor) {
let that = this; // 缓存当前promise实例例对象
that.status = PENDING; // 初始状态
that.value = undefined; // fulfilled状态时 返回的信息
that.reason = undefined; // rejected状态时 拒绝的原因
that.onFulfilledCallbacks = []; // 存储fulfilled状态对应的onFulfilled函数
that.onRejectedCallbacks = []; // 存储rejected状态对应的onRejected函数
function resolve(value) { // value成功态时接收的终值
if(value instanceof Promise) {
return value.then(resolve, reject);
}
// 实践中要确保 onFulfilled 和 onRejected ⽅方法异步执⾏行行,且应该在 then ⽅方法被调⽤用的那⼀一轮事件循环之后的新执⾏行行栈中执⾏行行。
setTimeout(() => {
// 调⽤用resolve 回调对应onFulfilled函数
if (that.status === PENDING) {
// 只能由pending状态 => fulfilled状态 (避免调⽤用多次resolve reject)
that.status = FULFILLED;
that.value = value;
that.onFulfilledCallbacks.forEach(cb => cb(that.value));
}
});
}
function reject(reason) { // reason失败态时接收的拒因
setTimeout(() => {
// 调⽤用reject 回调对应onRejected函数
if (that.status === PENDING) {
// 只能由pending状态 => rejected状态 (避免调⽤用多次resolve reject)
that.status = REJECTED;
that.reason = reason;
that.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(cb => cb(that.reason));
}
});
}
// 捕获在excutor执⾏行行器器中抛出的异常
// new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// throw new Error('error in excutor')
// })
try {
excutor(resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}
Promise.prototype.then = function(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const that = this;
let newPromise;
// 处理理参数默认值 保证参数后续能够继续执⾏行行
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === "function" ? onFulfilled : value => value;
onRejected = typeof onRejected === "function" ? onRejected : reason => {
throw reason;
};
if (that.status === FULFILLED) { // 成功态
return newPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
try{
let x = onFulfilled(that.value);
resolvePromise(newPromise, x, resolve, reject); //新的promise resolve 上⼀一个onFulfilled的返回值
} catch(e) {
reject(e); // 捕获前⾯面onFulfilled中抛出的异常then(onFulfilled, onRejected);
}
});
})
}
if (that.status === REJECTED) { // 失败态
return newPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onRejected(that.reason);
resolvePromise(newPromise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch(e) {
reject(e);
}
});
});
}
if (that.status === PENDING) { // 等待态
// 当异步调⽤用resolve/rejected时 将onFulfilled/onRejected收集暂存到集合中
return newPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
that.onFulfilledCallbacks.push((value) => {
try {
let x = onFulfilled(value);
resolvePromise(newPromise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch(e) {
reject(e);
}
});
that.onRejectedCallbacks.push((reason) => {
try {
let x = onRejected(reason);
resolvePromise(newPromise, x, resolve, reject);
} catch(e) {
reject(e);
}
});
});
}
};

